The durability of metal zipper sliders is one of the key factors affecting the performance and life of zippers. By optimizing the design and selecting the right materials, the durability of metal zipper sliders can be effectively improved to ensure that they maintain good function and appearance during long-term use.
Common materials for metal zipper sliders include brass, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, etc. Different metal alloys have different mechanical properties and corrosion resistance:
Brass has good corrosion resistance and strength, suitable for more conventional zipper use environments, but may corrode in high humidity or strong acid environments.
Stainless steel has extremely strong corrosion resistance and high strength, suitable for marine environments or extreme weather conditions, especially in high humidity or salt water environments, stainless steel zipper sliders have a long service life.
Aluminum alloy is light and has a certain degree of corrosion resistance, suitable for lightweight or high-end zipper products, but is relatively soft and easy to wear, suitable for low-wear environments.
Zinc alloy has good impact resistance and wear resistance, suitable for most conventional environments, and has a low manufacturing cost, suitable for the mid-to-high-end market.
By rationally selecting materials of different alloys, the most suitable material can be selected according to the use environment, functional requirements and cost constraints of the slider to improve the durability of the slider.
Surface treatment is a key means to improve the durability of metal zipper sliders. Common surface treatment methods include:
Electroplated metals (such as nickel, electrochromium, etc.) can enhance the corrosion resistance, wear resistance and aesthetics of the slider, especially the nickel electroplated surface has a strong antioxidant ability.
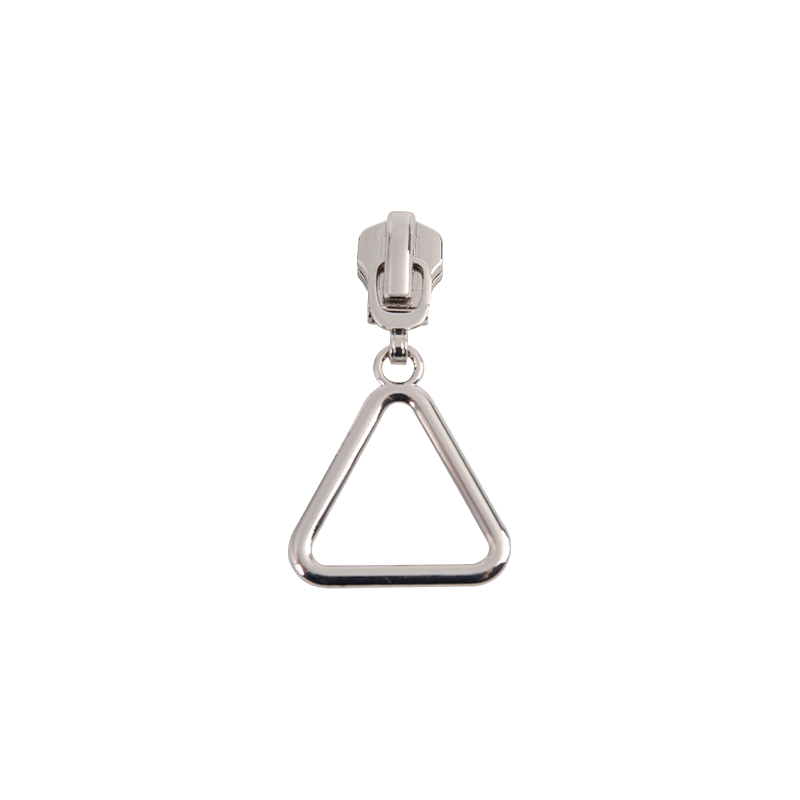

Anodizing For aluminum alloy sliders, anodizing can be used to increase its surface hardness and corrosion resistance. At the same time, anodizing can also enhance the appearance and increase the diversity of colors.
Spraying and coating treatment For the surface of the slider, spraying, sandblasting or other coating technologies can be used to increase the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the slider, especially for zipper sliders often used in harsh environments.
The design of the slider directly affects its load-bearing capacity and service life. Reasonable structural design can enhance the strength and stability of the slider and reduce wear in long-term use:
The outer shell of the slider should be designed to have sufficient strength to avoid deformation or breakage due to external impact. For sliders that need to withstand large pulling forces or be used repeatedly, increasing the thickness of the material and strengthening the bearing capacity of the structure are effective design methods.
Reducing the friction between the zipper slider and other components during use through a streamlined design helps reduce friction and extend the service life of the contact surface between the slider and the zipper tape.
The matching accuracy between the slider and the zipper tape is crucial to the smoothness and durability of the zipper. When designing, the friction between the slider and the zipper tape can be reduced by optimizing the shape of the contact surface, reducing the wear rate.
The mechanical structure inside the slider (such as the guide rail and gear design) should be designed more accurately to ensure that the slider and the zipper tape fit tightly and reduce damage caused by mechanical failure or friction.
Designing a self-lubricating device or adding a lubricating coating inside the slider can reduce friction with the zipper tape and effectively extend the service life of the zipper slider.
By comprehensively considering the above design optimization and material selection, the durability of the metal zipper slider can be greatly improved, thereby extending its service life and improving the overall performance and quality of the zipper product.

 en
en  русский
русский 한국어
한국어 get a free quote
get a free quote